Blood donation is a mighty deed to pass love on. The production of every blood product undergoes stringent complex procedures and also quality control to ensure the safety of blood donor and recipient. The whole 10-stage process takes around eight days from blood collection, delivery to laboratory, testing, production of blood component, storage, distribution, delivery to hospital, and finally utilisation by patient.
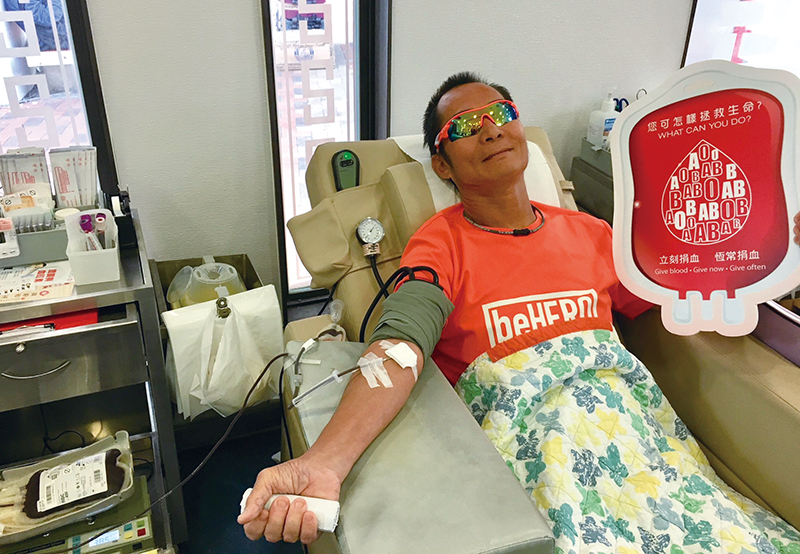
Blood collection
Donor visits a donor centre or mobile donation site. After completing a blood donation registration form, he will take a haemoglobin test. A nurse will conduct health screening assessment with body temperature taken, blood pressure checked and skin disinfected. Blood sample is taken for various tests. If the person is eligible for blood donation, the process then starts, which usually takes about seven to twelve minutes.
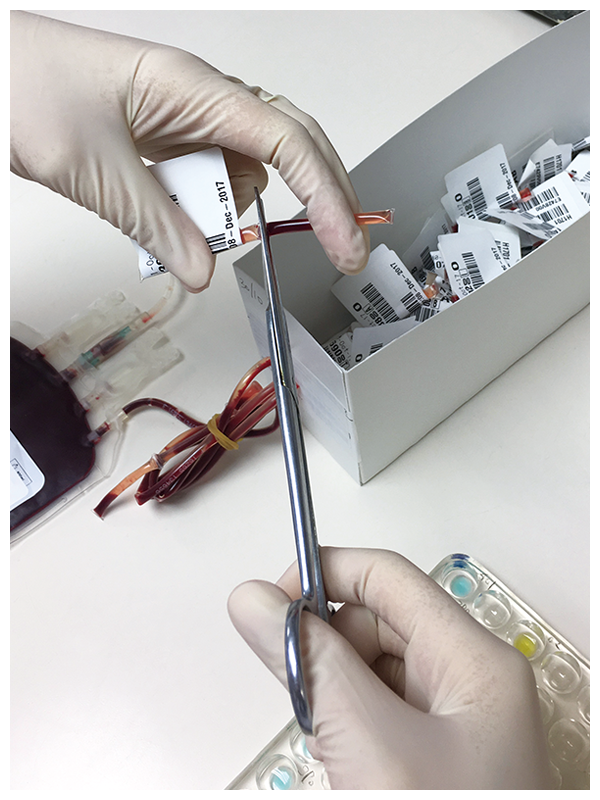
Delivery to laboratory
Blood collected is individually packed and stored in a temperature-controlled storage box with the corresponding blood sample before delivering to laboratory in BTS headquarters.
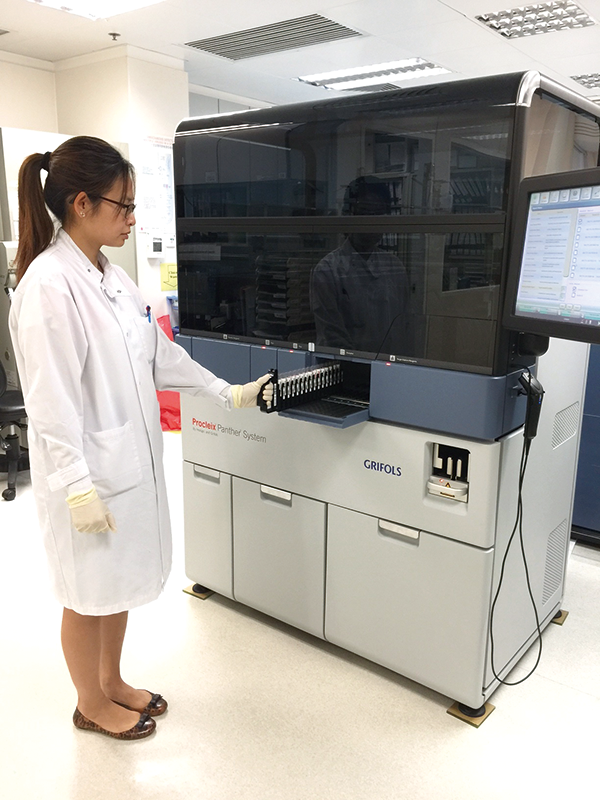
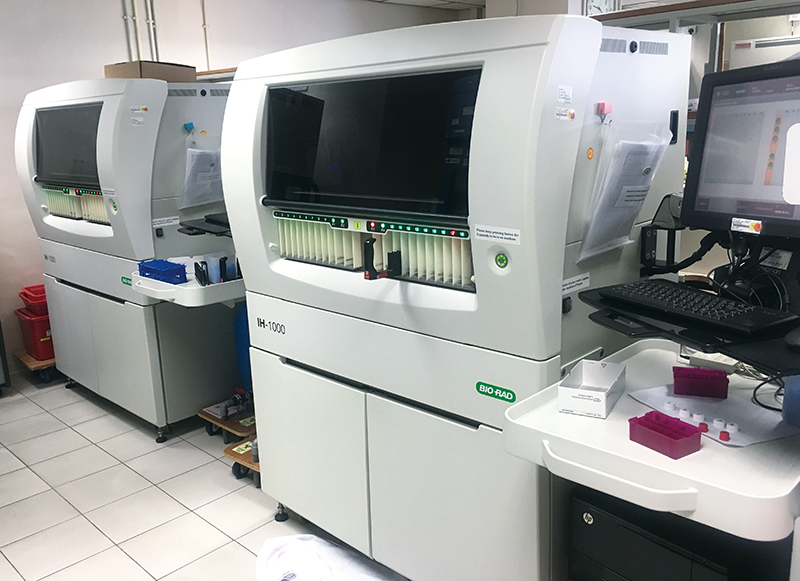
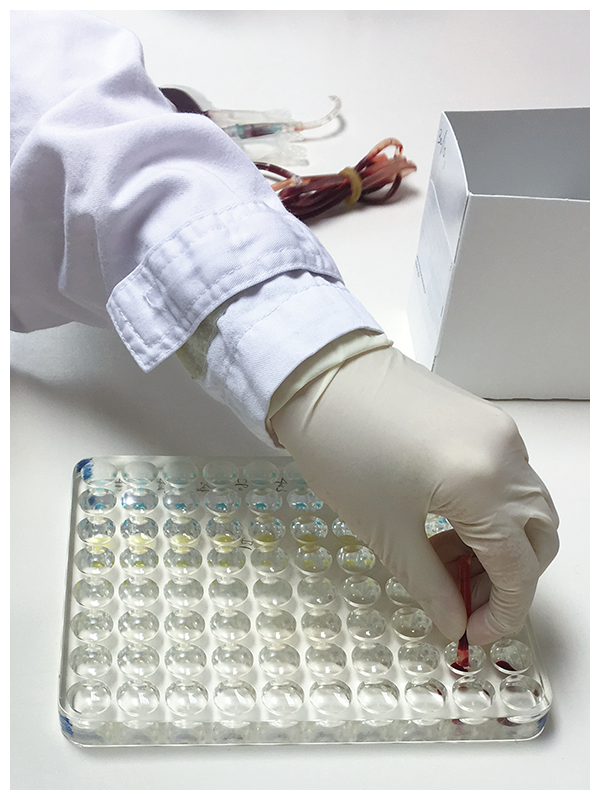
Testing
With an automated testing system in the BTS laboratory, blood collected undergoes blood grouping and tests for viruses of blood-borne infectious diseases, namely HIV antibodies, antigen and ribonucleic acid (RNA), Hepatitis B surface antigen and deoxyribonucleic acid, Hepatitis C antibodies and RNA, Human T-Lymphotropic Virus antibodies and Syphilis antibodies. Bacterial surveillance for platelet concentrates is also needed to ensure no contamination.
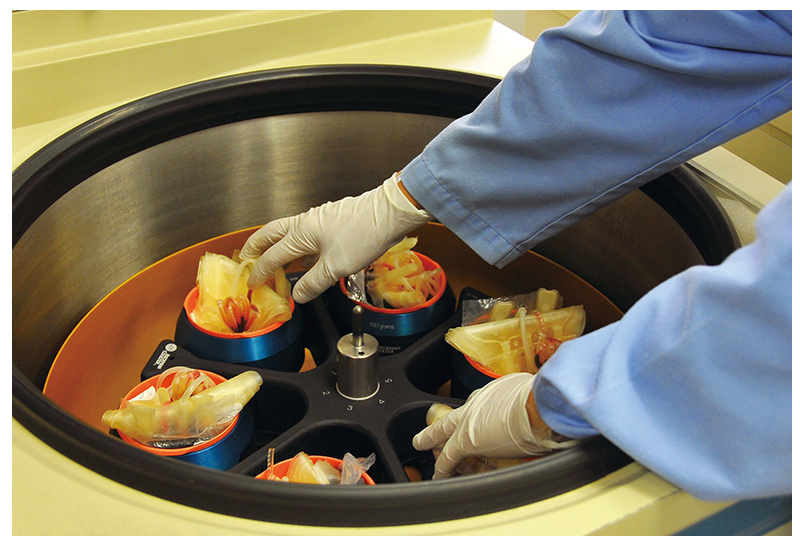
Stratification
Different blood components in the blood bag are stratified by a centrifuge. Red blood cells, white blood cells, plasma and platelets are separated to produce different blood products.
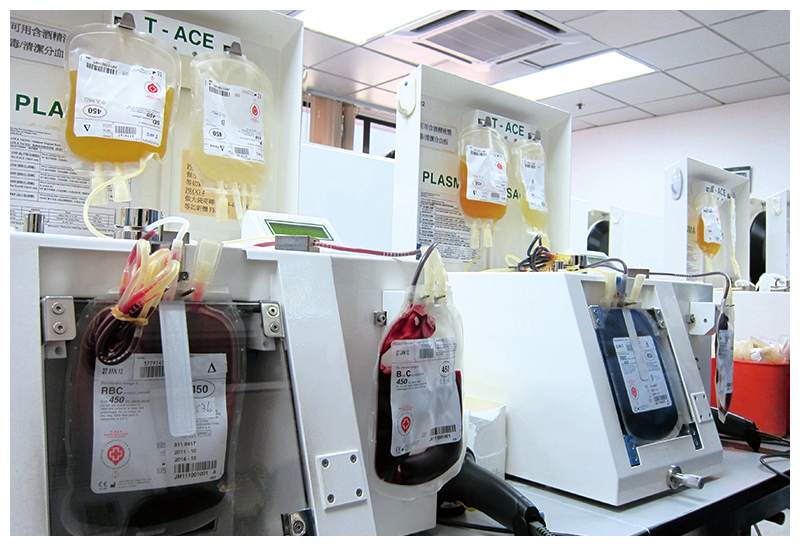
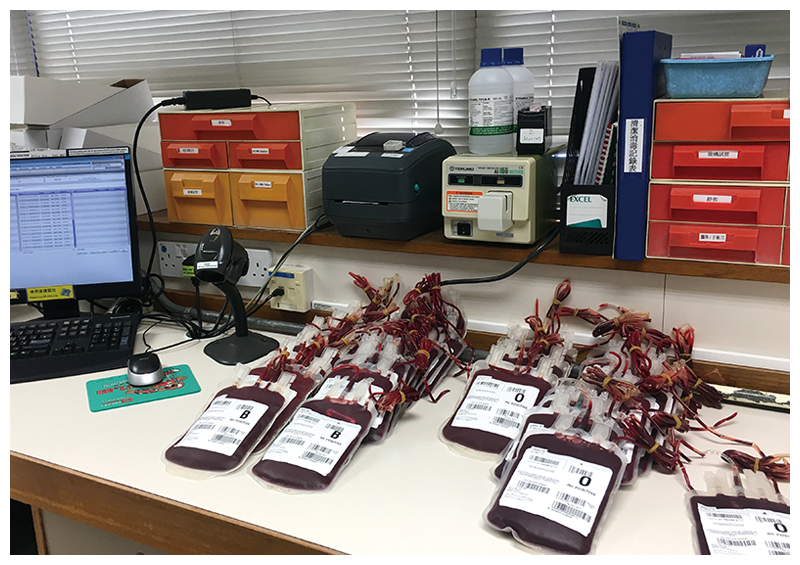
Labelling
Labels are put on every blood product. These labels include a barcode for donor identification, product information, blood group and other important messages such as collection date and expiration date.
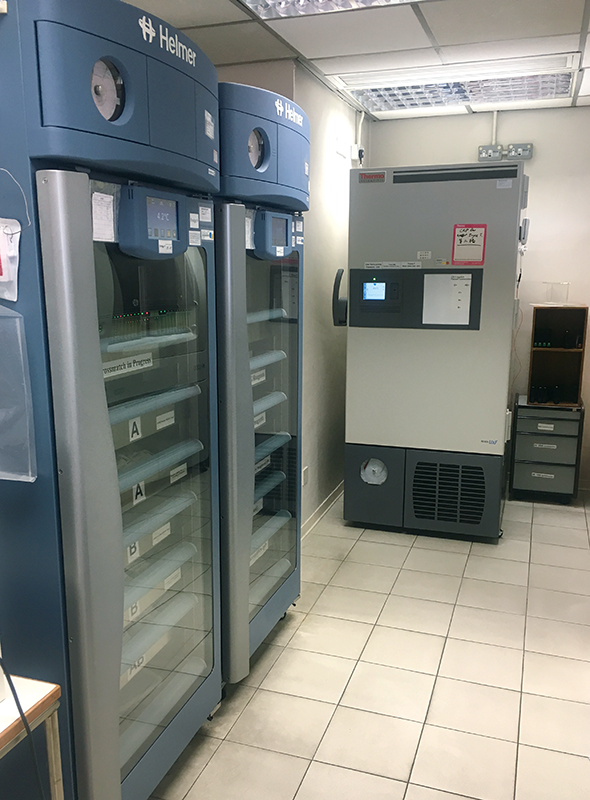
Storage
Blood products with different shelf life are stored at specific temperatures. Red blood cells with shelf life of 42 days are stored at temperature between 2℃ to 6℃. Plasma products having shelf life of one year are stored in freezer at -70℃ while platelet products with shelf life of five days are stored in platelet agitator at 22℃.
Distribution
Hospitals submit monthly forecast plan of the coming year based on blood utilisation of the previous year and also change in hospital services. BTS provides 24-hour service for all hospital blood banks in Hong Kong, and supplies blood products to hospitals daily or on alternate day. For instance, the Princess Margaret Hospital blood bank receives an average of around 100 units of blood products daily with a three-to-five-day inventory. Details of each blood product are recorded in computer system before delivery. The blood products are packed in sterilised boxes for delivery to hospital blood banks.
Receipt and verification
Upon receipt of blood products, hospital blood bank staff scan the barcode to check details against computer record, and verify the blood type of all red cell units within 30 minutes. Lastly, the blood products of respective blood group and expiry date are stored in 24-hour temperature monitored equipment according to different storage requirements.
Cross-matching
Utilisation at the frontline – when blood transfusion is required under general condition, e.g. scheduled procedure or surgery, medical staff reserve the quantity of blood products needed through the hospital computer system. Blood sample from patient is collected and sent to blood bank for testing. Tests are performed by blood bank staff to identify blood group and antibody and appropriate blood units are selected for cross-matching. Blood bank then notifies the medical team via computer system when the required blood units are ready to be collected.
In case of emergency such as civil disaster or traffic accident, medical staff will collect unmatched red blood cells of blood type O, which is considered suitable for universal use, in blood transfusion during resuscitation. Meanwhile blood sample of patient is collected and sent to blood bank for urgent testing and cross-matching for further blood products reservation if necessary.
If inventory of the blood bank runs low, the blood bank staff will send request to BTS and arrange with the hospital transport team to top up the blood stock level immediately.
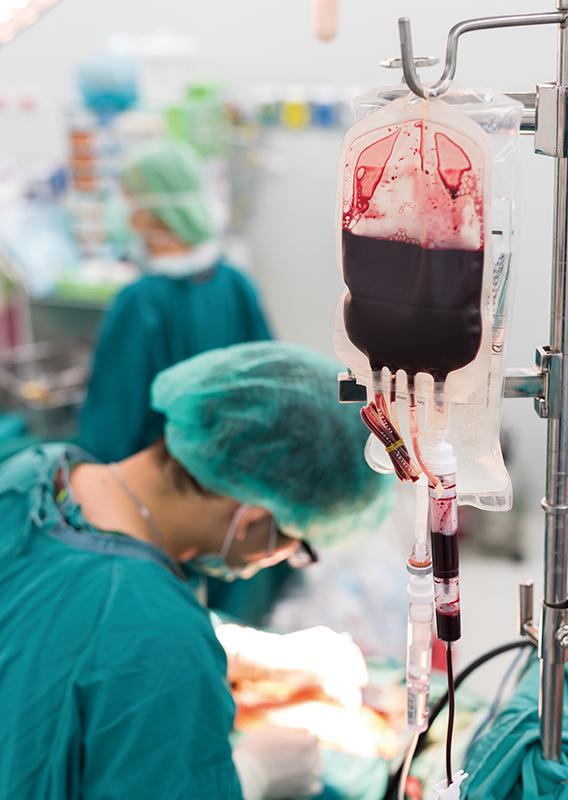
Transfusion
Medical staff check patient’s temperature and basic vital signs, positively identify the patient and verify information on the patient’s wristband to ensure compatibility with that on the blood bag and the transfusion note before infusion of blood. Patient’s reaction to blood transfusion, the beginning and ending time of transfusion are recorded on the medical record. The life-saving mission is accomplished.
COVER STORY
● More blood donors make mission possible
● Worker’s life saved after emergency blood transfusion
● From donor to recipient: 10-step journey
● All you want to know about blood donation
● Lesser known stories of blood donation
FEATURE
● Flashback: Recount of hospital development in Kowloon Peninsula
● History of QEH in 120 pictures
● Elders fight depression the nouveau way
● Elderly Council helps regain dignity and confidence
HELEN HA
WHAT'S NEW
● Collaboration key to preparedness for winter surge
STAFF CORNER
● Eat smart and fight flu! – Recommendations from Chinese medicine practitioner
● Eat smart and fight flu! – Recommendations from dietitian
● Policy Address supports HA with new funding
● 舌尖上的人情味 (Chinese version only)