Understanding hip replacement
Educational Video
(Chinese version only)
What is Hip Arthritis?
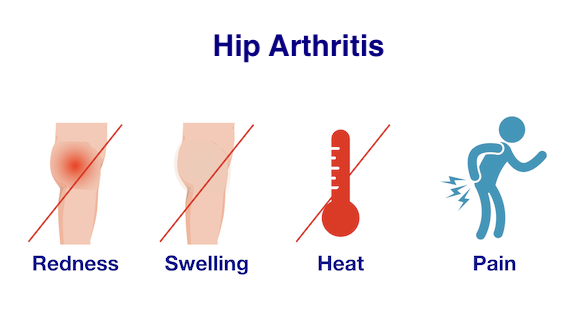
Hip arthritis, which can be caused by degeneration, inflammation and infection presents with pain in the hip joint. While the hip joint is surrounded by muscles, ligaments and tendons, symptoms including swelling and feeling of warmth in the joint are not noticeable.
What is Hip Osteoarthritis?
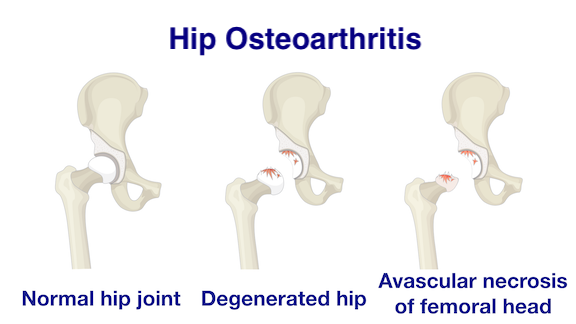
Hip degeneration is commonly caused by developmental hip dysplasia and avascular necrosis of femoral head in our locality. The weight bearing cartilage is worn faster than the reparative process. The muscle, ligaments and bone around the hip are also affected. All these are the contributing causes of osteoarthritis.
Hip Replacement Surgery
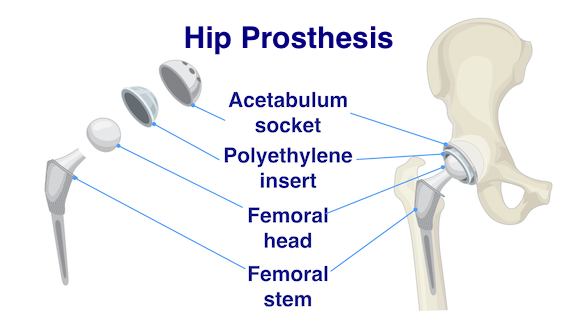
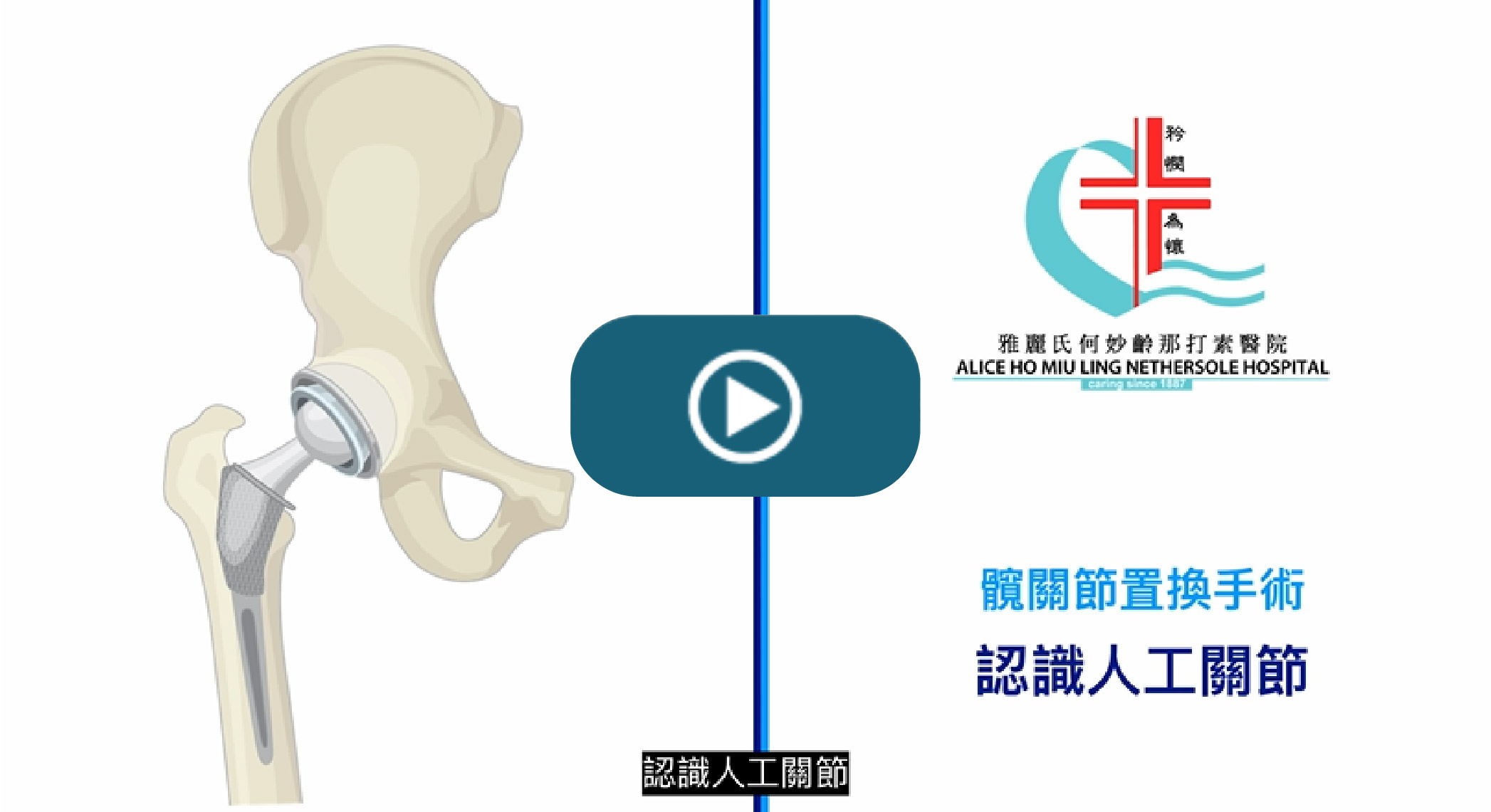
Total hip replacement is a surgery to remove the worn-out or damaged bone and cartilage, and the affected joint is replaced with an artificial implant. The fixation of the implants can be done by either cemented or cementless method. An artificial joint consists of two components:
- Femoral implant is composed of ball head and femoral stem. The ball head is made of metal or ceramic and the stem is made of metal.
- Acetabular implant (bowl shaped) is composed of liner and metal cup in cemenless fixation. The liner is made of polyethylene ( commonly known as plastic ) or ceramic. A plastic cup is applied on cemented fixation.
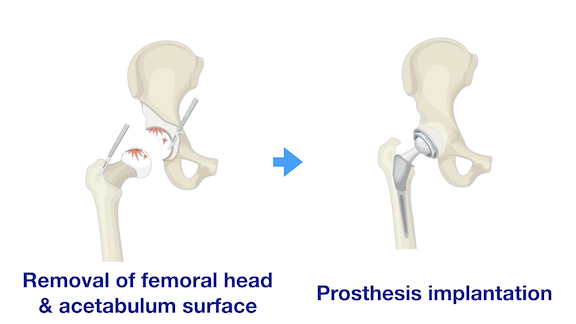
Operation Procedure
- According to the clinical condition, a surgeon will choose a surgical approach for performing total hip replacement, including posterior approach, anterior approach and lateral approach.
- The femoral head is firstly dislocated from the acetabulum and then cut off.
- Prepare the acetabulum surface which will be fixed to a suitable-size of acetabular implant.
- Cancellous bone inside the femoral canal is removed. A suitable-size femoral stem is inserted to the femoral canal and fixed. An appropriate ball head is put on the stem.
- The ball head is then fitted into the acetabulum cup. The hip joint mobility and stability are examined.
- A drainage tube may be placed near the wound. The surgical wound is closed.
- The lower limb will be bandaged if necessary.
Surgical Risks and Complications
General Complications
- Wound infection
- Post-operative chest infection
- Myocardial infarction
- Stroke
Surgical Risks and Complications
- Bleeding
- Nerve and vessels injury
- Prosthetic joint infection
- Joint dislocation
- Deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism
- Limb length inequality
- Hip stiffness
Disclaimer
The Department of Orthopaedics and Traumatology and the Physiotherapy Department of the Alice Ho Miu Ling Nethersole Hospital would try to ensure the accuracy of information provided on the website. The information contained in the videos and other content on the website has been made available for reference only, and is not intended to be a substitute for diagnosis or prevention of any disease. If any person feels unwell, please seek medical advice promptly to receive timely and appropriate treatment. If you have any questions about the video content and other information on the website, please consult a registered doctor or nurse.
The Alice Ho Miu Ling Nethersole Hospital hereby disclaims any and all liability to any party for any direct, indirect, implied, special, incidental or other consequential damages arising directly or indirectly from any use of the video content and other information, which are provided as are, and without warranties.
Copyright © 2020 The Physiotherapy Department of the Alice Ho Miu Ling Nethersole Hospital. All rights reserved.
¡@